How to protect offline backups
July 25, 2024 •

Offline backups are a common security tool to ensure your organization can recover from ransomware attacks. Yet many organizations don’t know how to completely protect offline backups.
In this article, we’ll unpack what an offline backup is, the ways to protect offline backups, and additional security measures you may not have considered.
Table of Contents
- What is a backup?
- What is an offline backup?
- How are offline backups protected?
- How to completely protect offline backups
What is a backup?
A backup is a copy of some or all of your organization’s data that is saved at regular intervals. Backups are strongly recommended as a baseline security measure that allows an organization to recover in the event of data loss from a ransomware attack, or other cyber event.
When it comes to backups, many cybersecurity professionals recommend the 3-2-1 rule to ensure proper backup procedures.
What is the 3-2-1 backup rule?
The 3-2-1 rule means you should have three copies of your data, stored using two different data types, and one of them should be off-site.
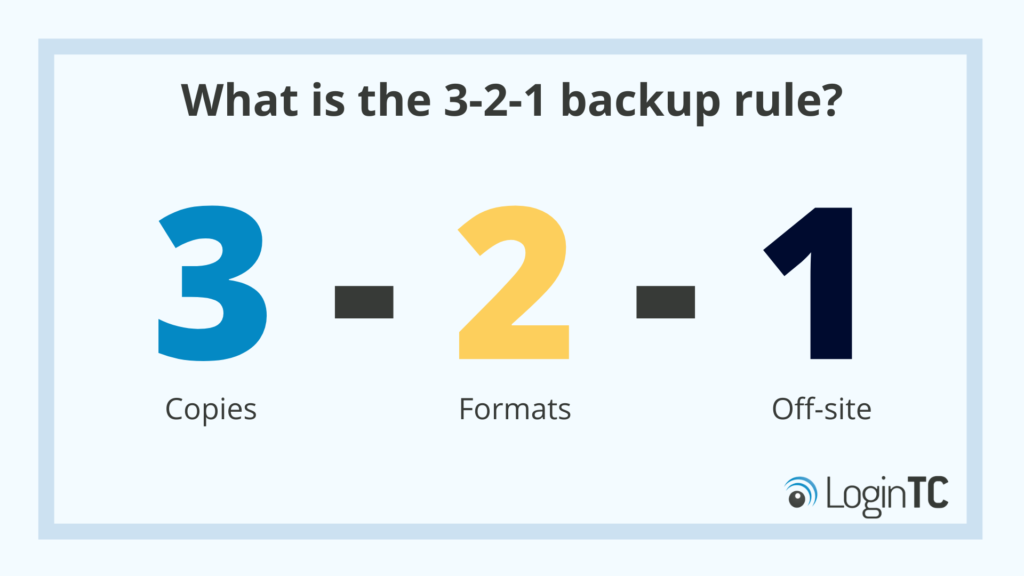
This ensures that you can rely on multiple copies of your data, some of which are saved in a different format in case one format fails. An off-site backup means that even if you suffer a physical security breach or incident, data can always be recovered from that separate location.
To meet this goal, many cybersecurity professionals recommend ensuring that one of the types of backups is an offline backup.
What is an offline backup?
An offline backup is when data is stored in a way that computers do not need an internet connection to access it.
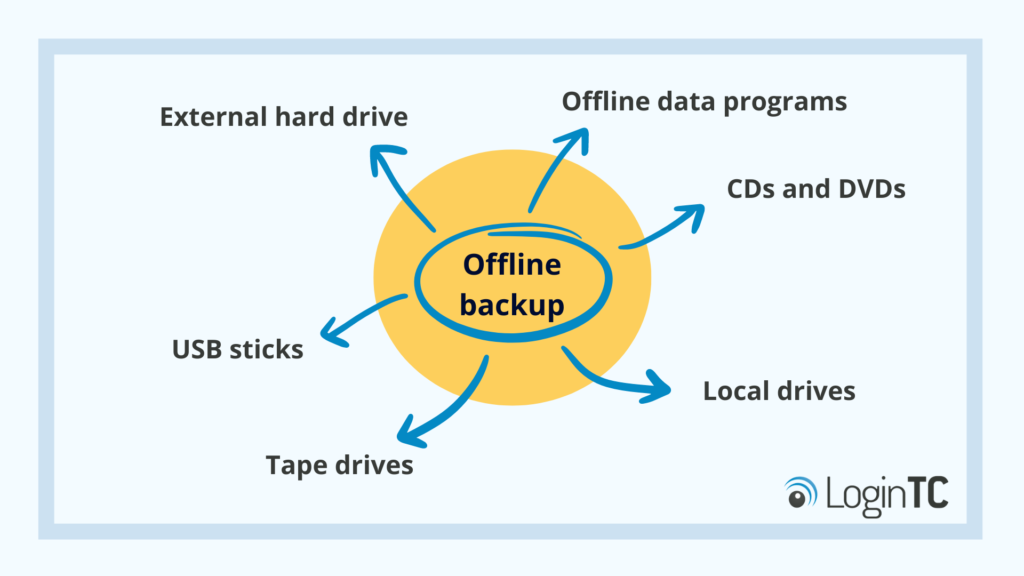
Common ways to store backups offline include:
- External hard drive
- USB sticks
- Tape drives
- CDs or DVDs
- Local drives
Offline backups provide protection in the event of ransomware attacks, as attackers are not able to access them through the network-based methods they used to take hold of systems in the first place.
Advantages and disadvantages of offline backups
Having a copy of your data stored offline, rather than in the cloud or otherwise accessible over the internet, ensures that your data can’t be compromised remotely. The backup will also not be impacted by internet outages, making it often more reliable than an online or cloud-based backup.
Conversely, offline backups may be less immediately available, owing to the fact that you have to retrieve the information from a physical or offline location. Offline backups also commonly require downtime in order to perform the backup and restore the data.
It’s up to the IT administrator to decide what kind of backup is best for their organization.
Air gapped vs. offline backups
Many people may use the terms air gap and offline interchangeably, but is there a difference?
Air-gapped backups are physically separated from external or online access at all times. Unlike offline backups which can occasionally be connected to the internet, air gapping ensures complete isolation of the data.
While air gapping is used in high-security environments, such as critical infrastructure, offline backups are sufficient security for most organizations.
Immutable vs. air gapped vs. offline
Another term you may see that relates to offline backups is an immutable backup. An immutable backup is a type of backup that cannot be rewritten or modified once it has been created.
Immutable backups are often created using Write Once Read Many (WORM) storage methods, in order to prevent the data from being altered or deleted.
Offline backups for cyber insurance
Increasingly, offline or immutable backups are being considered a minimum cybersecurity controls in order to access cyber insurance policies from major carriers.
It’s important to understand not just what your cyber insurance provider requires you to have in place for backups, but how those backups need to be protected.
How are offline backups protected?
While offline backups are a great start to making your organization more secure, it’s not enough to simply have them — they also require protection.
There are three different types of security controls you should consider adding to your offline backups:
- Physical controls: If your data is stored on physical devices, then they need to be physically secured. Think about how physical access to your data could be locked down or monitored with surveillance, both on-site and off-site.
- Technical controls: If a malicious actor is able to gain access to backups, implementing technical controls like encryption can ensure sensitive data remains unreadable.
- Administrative controls: Determine who should have access to the backups, and implement access controls based on those rules or roles. Consider additional identity and access controls like multi-factor authentication (MFA).
When deciding which controls to implement, it’s important to consider the compliance standards your organization must meet, your cyber insurance requirements, and any other security directives from regulatory bodies.
You should also design your offline backup protections in line with your organization’s existing or desired cybersecurity plan and protocols.
There are some enhanced security measures you may want to consider when designing offline backup protections.
How to completely protect offline backups
While no security tool is a silver bullet to protect against any kind of attack, there are ways to ensure more complete security of your organization’s data.
That’s why cybersecurity experts are recommending a move towards defense-in-depth and zero-trust principles. These principles introduce a layered approach that ensures security is implemented at each possible point of entry or access.
Let’s illustrate this approach using a specific security control: multi-factor authentication (MFA).
MFA for offline backups
Say your organization uses a tool like Veeam, which is installed on Windows machines, in order to manage backups, including offline backups.
The first step to protecting the backups through Veeam is to add an MFA requirement for accounts logging into the direct Veeam application.

However, in a zero-trust or defense-in-depth approach, that alone is not enough to protect the backups. That’s because the Windows machine that the Veeam application is installed on is still accessible.
MFA for privileged access
In order to implement a zero-trust approach to protecting offline backups, MFA should also be required to access the Windows machine that the Veeam application is installed on.
This introduces stronger privileged access security, something that many regulatory standards and cyber insurers also require.
Offline MFA
Finally, in the event that a cyber event or ransomware attack brings down your internet, a good defense-in-depth approach would ensure that MFA-protected access to critical infrastructure can be achieved offline.
Offline MFA guarantees that even if your internet access becomes unreliable, your ability to access Windows devices is not impacted.
Conclusion
There are many elements to consider when implementing proper protections for your offline backups. Choosing the right security controls that will meet relevant security requirements, and work with your users needs, can be difficult.
If you’re looking for advice about how to protect your offline backups, you can book a no-commitment consultation with our team.