MFA for air-gapped network security
January 20, 2025

When designing air-gapped network security controls, one aspect that is often overlooked is the need for multi-factor authentication (MFA).
While air-gapped networks are effective in protecting highly sensitive data and critical systems, it’s integral to not leave them susceptible to attacks they can’t fight on their own.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss how MFA can add critical security protections to your air-gapped environment, without introducing any new vulnerabilities.
Table of Contents
- What is air-gapped network security?
- Limitations of air-gapped networks without MFA
- The role of MFA in air-gapped networks
- LoginTC Managed: The ideal MFA solution for an air-gapped network
What is air-gapped network security?
An air-gapped network (sometimes also called air-gap, air wall, or disconnected network) is a type of network that is physically separated from other local networks or the internet. There is no connection, either wired or wireless, between the air gapped network and other networks/systems.
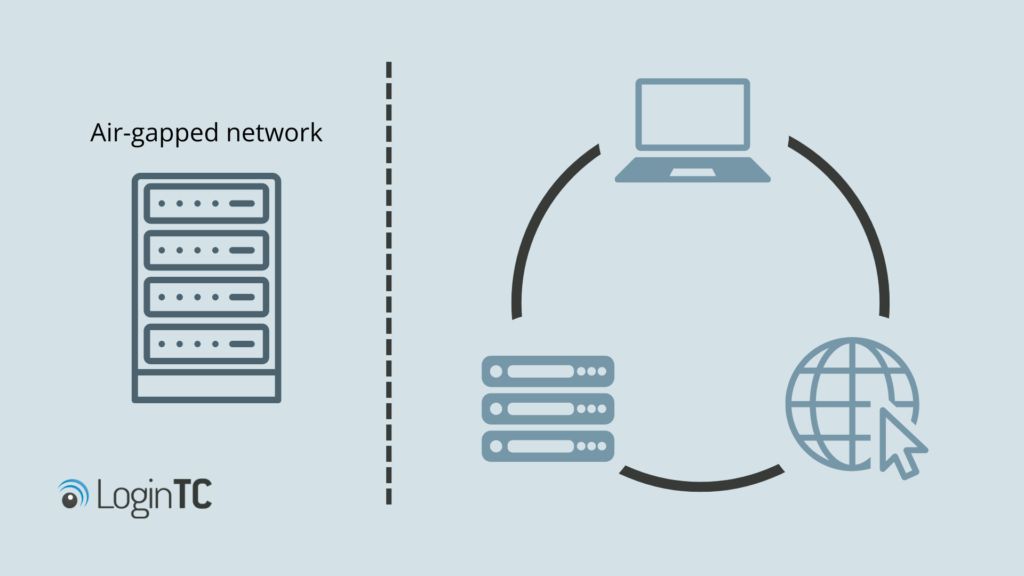
Typically, air gapped networks are used for backups that are held off-site in secure locations. As the network is disconnected from everything else, it is extremely difficult for malicious actors to remotely attack and gain access to it.
Air gapped networks are used in high-security industries like government, military, financial institutions and critical infrastructure.
These industries and others use air-gapped networks to secure what’s known as operational technology (OT), which control physical processes. These are mainly critical infrastructure resources which are highly sensitive and require additional security.
By air-gapping this technology from the rest of your environment, you can protect these critical assets from external threats and ensure they’re only accessed by authorized individuals.
However, all of this begs the question — what happens when you do need to access an air gapped network?
These networks still need to be managed and accessed by someone. Usually, this is by highly privileged accounts, which means there’s a need to ensure that account access is strongly protected.
How can you ensure your air gapped network can only be accessed by authorized personnel? The answer is MFA.
The limitations of air-gapped networks without MFA
While air gapping networks ensure they’re protected from remote attacks, vulnerabilities still lay in physical attacks. USB drives, manual data transfers, and insider threats all pose risks to air gapped networks.
Air-gap malware is a type of malware designed to specifically target air gapped networks.
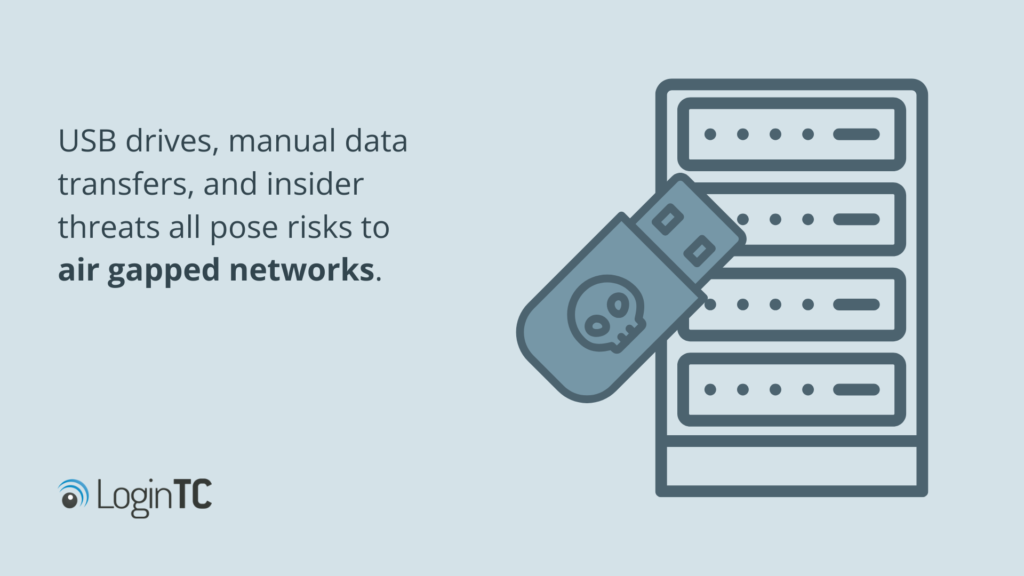
A recent example of this is when a European government organization’s air gapped network was repeatedly attacked between May 2022 and March 2024 using a compromised USB stick as the attack vector.
While air-gapped networks offer significant security benefits by physically isolating sensitive systems from the internet, they are not immune to security risks. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the physical environment, including insider threats, human error, or compromised access points. In these scenarios, even the strongest network perimeter defense can be bypassed.
This is where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) becomes essential.
The role of MFA in air-gapped network security
MFA adds an extra layer of security to air-gapped networks by requiring more than just a username and password for authentication.
MFA combines multiple factors—something the user knows (a password), something the user has (a mobile device or hardware token), or something the user is (biometric data)—to verify their identity. This significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access, as an attacker would need to compromise multiple authentication factors to gain entry.
In the context of air-gapped networks, MFA ensures that even if an attacker gains physical access to a network segment or device, they cannot easily breach the system without also having access to the required second factor.
This added layer of security is crucial, especially for preventing remote administrative access and protecting sensitive data from insider threats. MFA can also protect physical devices used in air-gapped environments, such as USB drives or external storage, which are often used for transferring data between isolated networks.
By implementing MFA, organizations enhance the security of their air-gapped networks, making it much more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access, even in the event of physical security breaches or insider collusion.
However, you need to ensure that MFA itself does not introduce additional external dependencies which can weaken air gapped networks. This problem can be solved by using a fully on-premises MFA solution like LoginTC Managed.
LoginTC Managed: The ideal MFA solution for an air-gapped network
LoginTC Managed is a comprehensive, on-premises MFA solution that enhances air-gapped network security. Unlike other SaaS MFA solutions, LoginTC Managed offers complete control to administrators without limiting them to unworkable or complicated authentication methods.
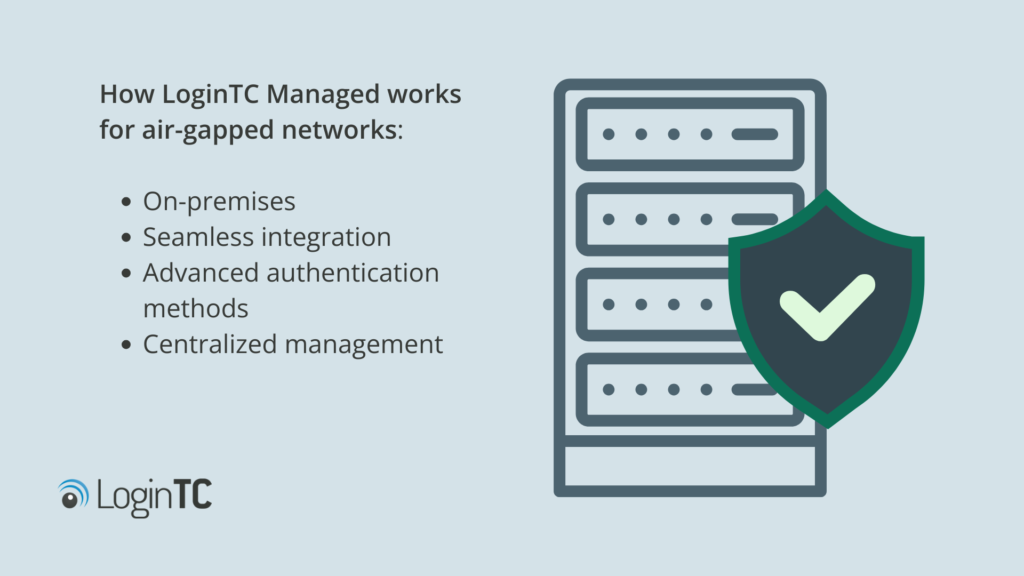
Here’s how LoginTC Managed works for air-gapped networks:
- On-premises control: With LoginTC Managed MFA solution, there’s no reliance on the internet or external cloud services. This means you’ll have zero external dependencies. Even upgrades can be done fully offline.
- Seamless integration: LoginTC Managed works with existing network security infrastructure, such as on-premises Active Directory. You can choose to deploy via a virtual appliance or as a standalone deployment.
- Advanced authentication methods: LoginTC Managed MFA supports phishing-resistant FIDO2 security keys, hardware and software one-time passwords (OTPs), passcode grids, and more. These offline methods offer flexibility and ease of use for end-users and administrators alike.
- Centralized management: The LoginTC Managed administrator portal provides full visibility and control over authentication processes, as well as streamlined user and token lifecycle management, without compromising on security in an air-gapped environment.
Additional considerations for securing air-gapped networks with MFA
In addition to implementing LoginTC Managed MFA to protect your air-gapped network, there are some additional best practices to consider:
- Assessment: An important first step in introducing new security controls into your air-gapped environment is to perform an MFA assessment. This assessment process helps ensure that MFA is applied to all entry points, including remote administrative access and physical devices used in the network. Check out our series on MFA assessments for how to get started.
- Audits: It’s important to conduct regular audits of access controls and MFA configurations. Within the LoginTC Managed portal you can review MFA policies and change settings to better suit your organization’s needs. Changes and updates can all be made offline.
- Employee training: An often overlooked step in introducing new security controls is the need to educate and train staff on the importance of the new controls, and how to properly use them. This training should also cover insider threats and how to be diligent against bringing in physical items, such as phones and USB sticks, to air-gapped environments.
Conclusion
Air-gapped networks play a critical role in safeguarding sensitive systems and data by isolating them from external threats. However, relying solely on physical isolation is not enough to protect against insider threats, compromised access points, and human error. Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) into air-gapped network security controls adds an essential layer of protection, ensuring that only authorized users can access critical systems, even in the most secure environments.
With LoginTC Managed, you get a robust, on-premises MFA solution designed specifically to meet the needs of air-gapped networks. By enhancing security without relying on internet connectivity, LoginTC Managed offers seamless integration, centralized management, and strong authentication capabilities tailored to the unique requirements of isolated environments.
Ready to secure your air-gapped network with LoginTC? Contact us today to get a free trial download package and experience how LoginTC Managed can enhance the security of your most critical systems.