Why Zero Trust MFA is essential for your business security
April 21, 2025 •

Imagine if you went to the airport and the one and only time they checked who you were, or what you were doing there, was right at the front door. This approach might stop some security threats, but this overreliance on one entry point leaves too much room for error, and threats could slip by. Plus, innocent travelers could end up at the wrong gates, or even on the wrong plane, without even realizing it.
Instead of this one-time check, airports implement multiple layers of security checks, ensuring at each step of the process that travelers are who they say they are, and are going where they need to go.
Cybersecurity is no different. When users and devices want to access a network, traditional security protocols often allow those devices access after one simple authentication check. Zero-trust security architecture is different.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what zero trust security is, and how to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to complement your zero trust security protocols.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity framework that assumes no user or device is inherently trustworthy. Each time a device is added to a network, or each time a user requests access to another part of the network, their identity must be re-verified.
What is Zero Trust MFA?
Zero Trust MFA is the implementation of a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system where a user is authenticated each time they login to an application or service within the network. Authentication is re-confirmed after each timeout, regardless of whether other conditions have changed.
This is in contrast to MFA policies which allow users to stay authenticated within certain time-windows, or as long as their login details, such as IP address or internet connection, have not changed.
Zero Trust MFA is often implemented in high-security environments or for specific compliance reasons.
Key principles of Zero Trust MFA
There are a number of key principles that form the foundation of any Zero Trust MFA system. These include, but are not limited to:
Verify Continuously: Authentication is not a one-time event. Continuous authentication occurs throughout the network at each new access point.
- Least Privilege Access: Users are only granted permissions to access the specific resources and privilege levels that they need for each task.
- Microsegmentation: Movement within networks is strictly managed in order to minimize attack surfaces and prevent horizontal attacks.
- Context-Aware Authentication: Factors like geolocation, device health, and behavioral patterns influence authentication decisions.
How to implement Zero Trust MFA effectively
Implementing a Zero Trust MFA strategy effectively requires careful planning and the right tools for the job. By following these steps, you can design a Zero Trust MFA implementation that works for your organization’s unique needs.
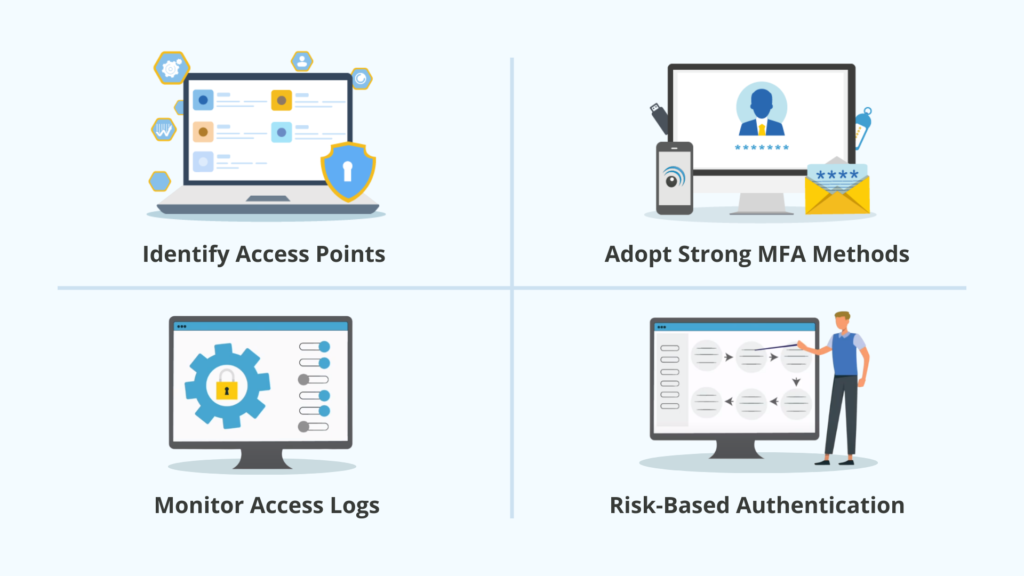
1. Identify Access Points
The first step to developing a comprehensive Zero Trust MFA implementation is to identify all access points into and within your network. Each device, VPN, firewall, remote access service, email account, or web application should have MFA added to logins for complete protection. This is where third-party MFA solutions, which offer one-token access across all applications and services.
2. Adopt Strong MFA Methods
Strong and simple to use authentication methods like push notifications, biometrics, and security keys will make frequent authentication streamlined for end users. These methods also allow for adaptive authentication that responds to risks and behavioral attributes, which is essential for a Zero Trust MFA implementation.
3. Monitor and Analyze Access Logs
To ensure real-time monitoring of access requests, use an MFA solution that has native reporting tools, as well as the ability to connect to reporting and auditing software using syslogs. This monitoring will allow you to identify suspicious login attempts.
4. Enforce Risk-Based Authentication (RBA)
Implementing risk-based authentication (RBA) allows you to dynamically adjust authentication requirements based on risk level of users dependent on a range of conditions or circumstances. Risk based authentication can take into account factors like the location, the time-of-day, or the IP address of the login attempt.
Cloud and On-Premises Zero Trust deployments
When implementing Zero Trust MFA, administrators should also decide how to deploy it: in the cloud, on-premises or hybrid. Either approach can support a Zero Trust model, but each offers different advantages depending on your organization’s needs.
Cloud-based MFA solutions are ideal for businesses looking for quick deployment, easy scalability, and minimal maintenance. They’re a great fit for distributed teams and organizations embracing remote or hybrid work.
On-premises deployments provide full control over your infrastructure—ideal for industries with strict compliance requirements or legacy systems. LoginTC Managed allows you to fully self-host MFA for Zero Trust architecture, giving you the control you need without sacrificing usability.
Overcoming common challenges
While Zero Trust architecture offers superior security protections, there can be some challenges in adopting it, especially when organizations are first implementing new security practices.
Ensuring that user friction is kept to a minimum will improve overall user experience, and user adoption of new security tools. Legacy systems are another challenge, as modern authentication tools can’t always integrate seamlessly. Additionally, while some Zero Trust MFA solutions can add to an additional cost, the full ROI of preventing costly data breaches should be factored into account.
The future of Zero Trust MFA
As Zero Trust MFA continues to rise in popularity, modern authentication tools like passwordless authentication, AI and machine learning, and continuous authentication processes will become more available and widely used.
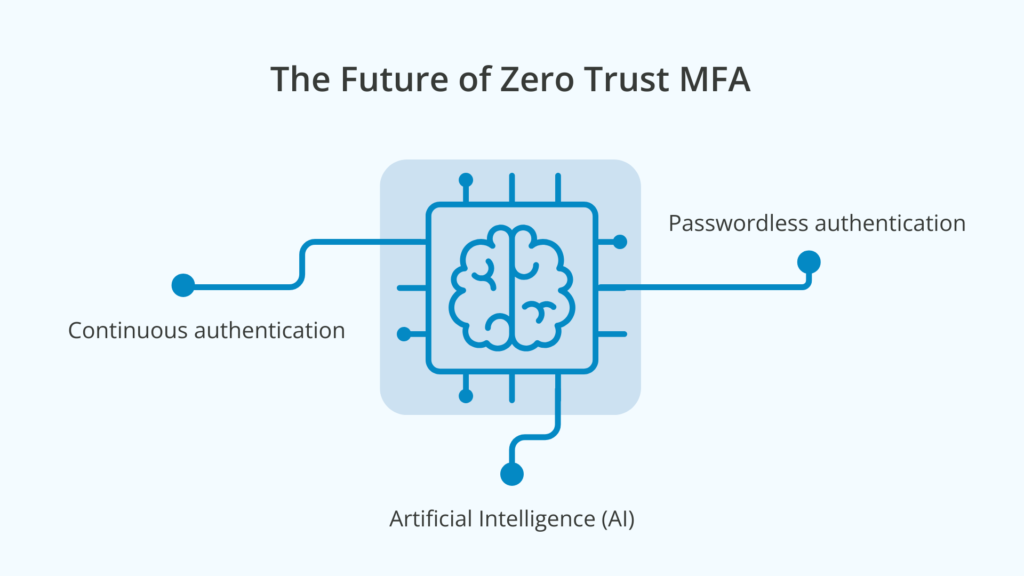
These advanced MFA capabilities offer even stronger security protection for high-security organizations that need to remain compliant and keep malicious attackers out of critical systems and operations.
Conclusion
In today’s ever-evolving threat landscape, traditional perimeter-based security is no longer enough. Zero Trust MFA provides a vital layer of defense by ensuring that only verified users can access critical systems—regardless of location, device, or network.
By embracing Zero Trust Architecture and implementing robust multi-factor authentication, businesses can drastically reduce the risk of credential-based attacks, enhance compliance, and stay resilient against modern cyber threats.
Don’t wait for a breach to take action—start your free trial of LoginTC today and take the first step toward a Zero Trust future.